What is a cell?
Discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 after observing cork under a microscope, the cell forms the basic unit of an organ. Although Hooke discovered dead cells, living cells were discovered a lot later. Depending on the number of cells, an organism can be multicellular (number of cells) or unicellular (single- celled). Let's learn more about the basic biology of all life:
The shape of cells vary according to their function. While single celled organisms are shapeless, nerve cells in humans have long branched structure. The components that make up a cell are enclosed in a membrane, termed as the cell membrane. It is responsible for determining the shape of the cell.


The size of a cell however varies but is independent of the size of an organism itself. Cells that perform a specific function form a tissue. The tissue collectively forms an organ and various organs having different functions form an organ system.
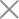
Parts of the cell
Cell Membrane, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Cell Wall
The cell membrane also called the plasma membrane forms the outermost layer in almost all the cells and inside it all other components are present. It is porous allowing exchange of material from one cell to another and at the same time keeps the cells separate from one another. In plants, cells also have a Cell Wall.
It is a protective covering lining the plasma / cell membrane which saves the cell from wear and tear due to a hostile environment as the plants are immobile and cannot change their position to find a safer environment to live like humans or animals can. The plasma membrane can be divided into: Cytoplasm and Nucleus.


Nucleus is the centrally located dense body within a cell while everything inside the cell membrane except the nucleus is the cytoplasm. Components present in cytoplasm are called organelles. Mitochondria, ribosomes, golgi bodies form the organelles.
Nuclear membrane is the outermost covering of a nucleus separating it from the cytoplasm. It also regulates the exchange of materials in and out the nucleus. The nucleus carries nucleolus (spherical body at the centre of the nucleus), chromosomes (thread-like structures) which carry genes. Blue green algae lack nuclear membrane and are termed as prokaryotes having prokaryotic cells. Rest all organisms usually have a well-organised nucleus and are called eukaryotes having eukaryotic cells.
How does cell-growth affect us?
In our daily life, we hear things like dead skin cells, etc. We study about cells and their functions to understand how important they are for us. Mostly green leafy vegetables, dairy products, pulses are rich in nutrients that help in proper growth and repair of cells.
Why is cell replication important? It keeps us healthy for a very long time. This process continues throughout our life only the rate of replication and regeneration slows down depending on the age. You must have come across older people who are surprisingly more energetic than most youngsters.


This is because they consumed and stored up a good amount of nutrition when their body could readily assimilate them. As a young teen or adult we are constantly kept away from junk food as the preservatives, food coloring present in these food items do not help the cells grow and the body gets weaker due to lack of proper nutrition.
So pay attention to what you consume. Good nutrition stays for life. Literally!